Design Pattern(12) - Adaptor
July 14, 2017以下文章是閱讀 深入淺出Design Pattern 還有 聖經還有Source making的筆記 圖片截圖自lynda.com的Foundations of Programming: Design Patterns 要更深入的理解一定要去看這兩本書
轉接器
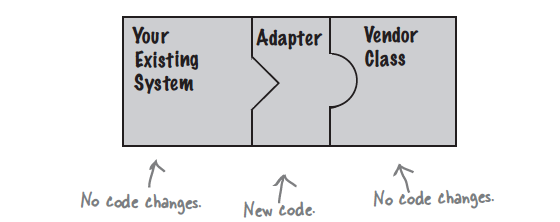
跟我們常用的電源轉接器一樣 電腦需要的電壓 跟你牆壁電源提供的電壓不一樣 你就需要一個AC Adaptor來改變電壓 讓電腦可以跟生活用電相容
OO Adaptor也一樣 從一個介面轉到另一個介面 讓兩者可以相容
掛羊頭賣狗肉
羊會叫 也會走
public interface Goat {
public void makeBleatSound();
public void walk();
}
public class WildGoat implements Goat {
public void makeBleatSound() {
System.out.println("bleat");
}
public void walk() {
System.out.println("I'm walking");
}
}狗會叫 也會跑
public interface Dog {
public void makeSound();
public void run();
}
public class Maltese implements Dog {
public void makeSound() {
System.out.println("Woof");
}
public void run() {
System.out.println("I'm running");
}
}我們今天想要掛羊頭賣狗肉的話 我們需要一個狗轉接器 這個轉接器需要實作羊 因為接下來client會把這個class生成的物件當作羊來用
public class DogAdapter implements Goat {
Dog dog;
public DogAdapter(Dog dog) {
this.dog = dog;
}
public void makeBleatSound() {
dog.makeSound();
}
public void walk() {
dog.run();
}
}Client怎麼用呢
public class GoatTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Maltese dog = new Maltese();
WildGoat goat = new WildGoat();
Goat dogAdapter = new DogAdapter(dog);
testGoat(goat);
testGoat(dogAdapter);
}
static void testGoat(Goat goat) {
goat.makeBleatSound();
goat.walk();
}
}bleat
I'm walking
Woof
I'm running這就是最基本的物件轉接器
轉接器模式
將一個類別的介面 轉換成另一個類別的介面供客戶使用 讓介面不相容的類別可以合作
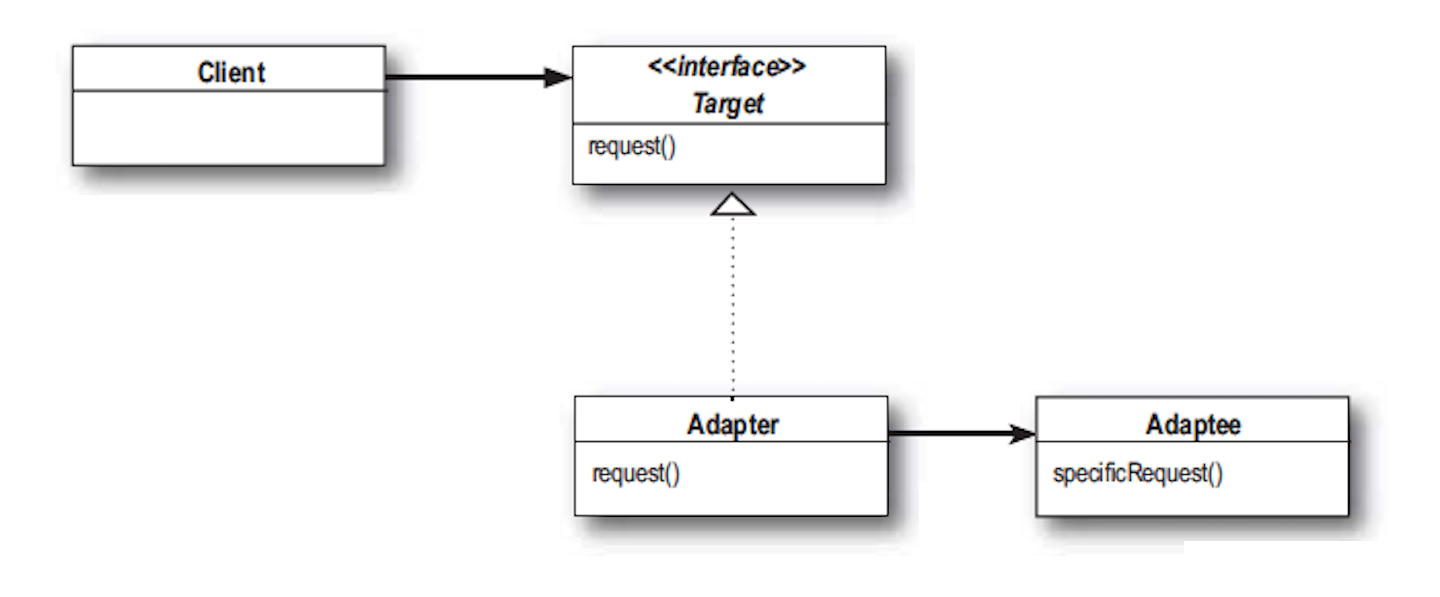
物件轉換器結構
-
Target(羊介面): 定義Client所用的介面 Adaptor需要實作這個介面
-
Adaptor(狗轉接器): 將Adaptee轉換成Target介面
-
Adaptee(狗介面) 需要被轉換的介面
-
Client(你): 使用Target介面
物件轉換器優缺點
1.一個Adaptor就可以處理所有的Adaptee和Adaptee的子類別
2.Adaptee可以是介面也可以是類別 Target其實也可以是介面也可以是類別 四種排列組合都可以
不信
不信我實作給你看 剛剛的DogAdaptor是兩個都是介面(實作1)
下面的code Adaptee是介面(Dog) Target是類別(WildGoat) (實作2)
public class DogWildGoatAdapter extends WildGoat {
Dog dog;
public DogWildGoatAdapter(Dog dog) {
this.dog = dog;
}
public void makeBleatSound() {
dog.makeSound();
}
public void walk() {
dog.run();
}
}下面的code Adaptee是類別(Maltese) Target是介面(Goat) (實作3)
public class MalteseAdapter implements Goat {
Maltese mal;
public MalteseAdapter(Maltese mal) {
this.mal = mal;
}
public void makeBleatSound() {
mal.makeSound();
}
public void walk() {
mal.run();
}
}下面的實作是Adaptee是類別(Maltese) Target是類別(WildGoat) (實作4)
public class MalteseWildGoatAdapter extends WildGoat {
Maltese mal;
public MalteseWildGoatAdapter(Maltese mal) {
this.mal = mal;
}
public void makeBleatSound() {
mal.makeSound();
}
public void walk() {
mal.run();
}
}因為在實作Adaptor的時候 對於Target的函式我們用了繼承 對於拿到Adaptee的函式我們用了合成(Composition)
因為用的是合成 所以Adaptee是越父類別越好 因為Adaptee的子類別也可以用父類別的Adaptor
實作2就是硬生生比實作4好用 實作1就是比實作3清爽
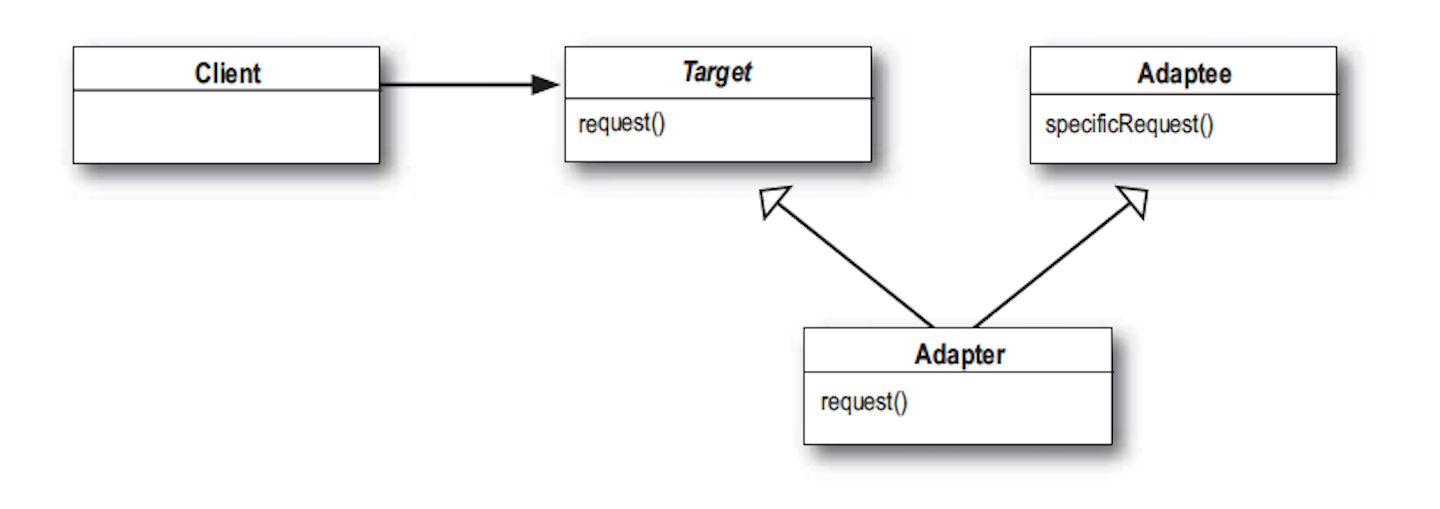
類別轉換器結構
還有另一種方法可以達到一樣效果 就是adaptor利用多重繼承
同時實作那兩個介面 然後再overwrite Target的函式 讓它去call Adaptee的函式
-
Target(羊介面): 定義Client所用的介面 Adaptor需要繼承這個interface
-
Adaptor(狗轉接器): 用Adaptee的函式實作Target介面
-
Adaptee(狗介面) 需要被轉換的介面 Adaptor需要繼承這個interface
-
Client(你): 使用Target介面
類別轉換器優缺點
1.類別轉換器因為Adaptor直接繼承了Adaptee 所以Adpator無法使用在Adaptee的子類別的函式
2.但是Apaptor可以overwrite Adaptee的函式
3.Adaptee必須是類別(才能繼承) java並不支援多重繼承 所以Target必須要是介面
public class MalteseGoatClassAdapter extends Maltese implements Goat{
public MalteseGoatClassAdapter() {}
public void makeBleatSound() {
this.makeSound();
}
public void walk() {
this.run();
}
}奇怪了 你剛剛的實作1實作2的Adaptee也都用介面 那現在怎麼說不能用介面?
做學問要追根究柢 要用也可以 只是Dog介面裡面的函數還是必須要有人來實作 你就被逼的只能在Adaptor實作
public class DogClassWildGoatAdapter extends WildGoat implements Dog{
public DogClassWildGoatAdapter() {}
//實作Dog的函式
public void makeSound() {
System.out.println("Woof");
}
public void run() {
System.out.println("I'm running");
}
//overwrite WildGoat的函式
public void makeBleatSound() {
this.makeSound();
}
public void walk() {
this.run();
}
}一個類別就該做一件事 Adaptor類別不應該去實作狗狗介面 所以類別轉換器還是乖乖繼承狗類別